EC2 Instance Creation and Configuration
10th July 2025
10th July 2025
Creating an AWS EC2 instance is a crucial skill for anyone looking to manage cloud infrastructure. This guide will walk you through the step-by-step process of creating and configuring an EC2 instance. By the end, you’ll have a fully operational server with Apache installed and secured using best practices.
Let’s dive in and learn how to leverage AWS EC2 to deploy and manage scalable applications efficiently.
Start by logging into your AWS Management Console and navigating to the EC2 dashboard. Choose the Ubuntu AMI for
a secure and flexible environment. Select the t2.micro instance type, which is suitable for
low-cost and lightweight applications.
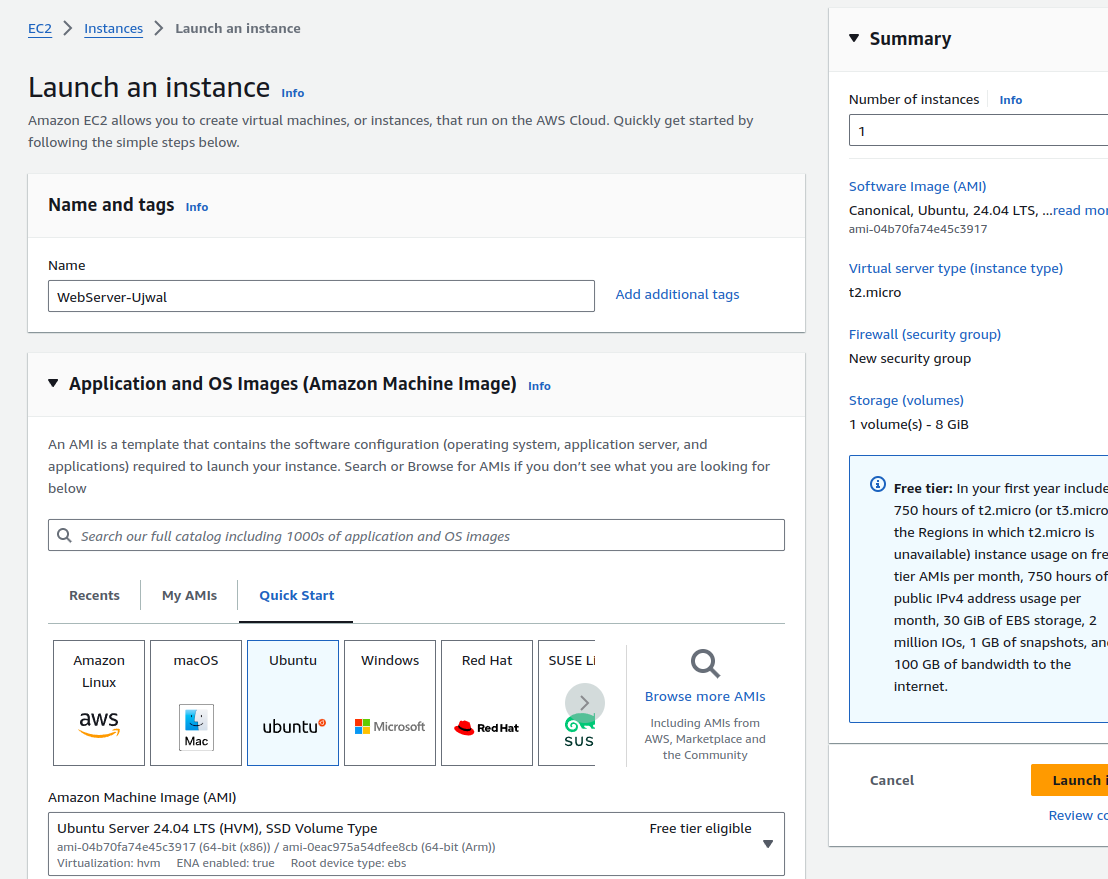
Once you’ve chosen the AMI and instance type, proceed to configure instance details. Add meaningful tags to identify your instance. For example:
Name, Value: My-EC2-InstanceEnvironment, Value: Production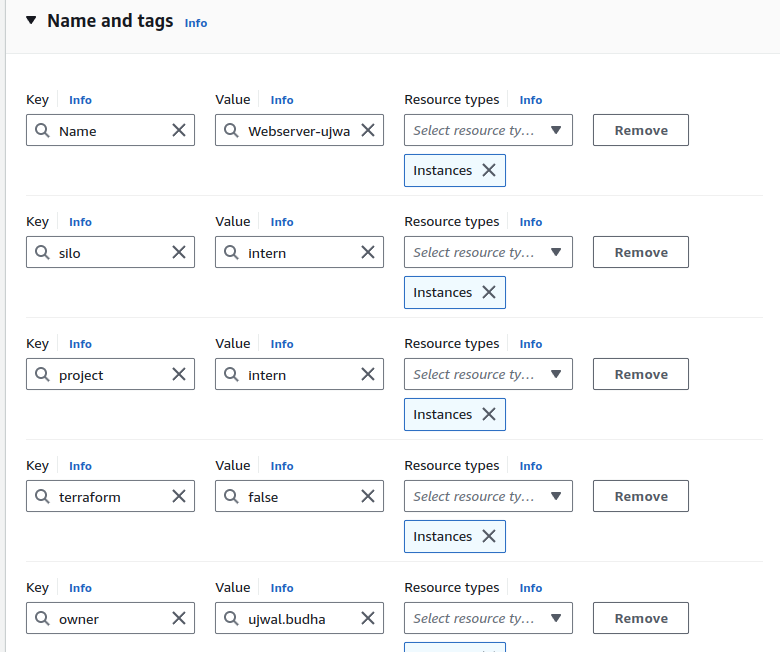
Security groups are essential for controlling inbound and outbound traffic to your EC2 instance. Create a security group with the following rules:
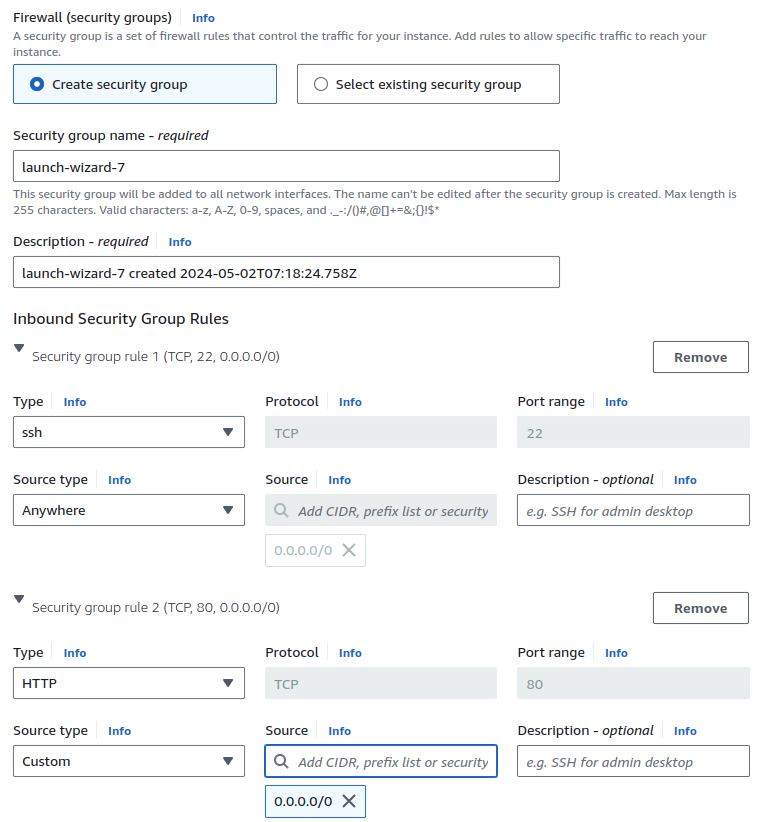
Generate or use an existing SSH key pair to connect securely to your instance. Ensure the key permissions are correctly set:
chmod 400 secretkey.pemOnce your instance is running, connect to it using the public IP address:
ssh -i "secretkey.pem" ubuntu@Use the following user data script to install and configure Apache during instance launch. This script ensures the web server is up and running as soon as the instance is initialized:
#!/bin/bash
sudo apt update -y
sudo apt install apache2 -y
sudo systemctl start apache2
sudo systemctl enable apache2
After the instance starts, verify its status in the AWS Management Console:
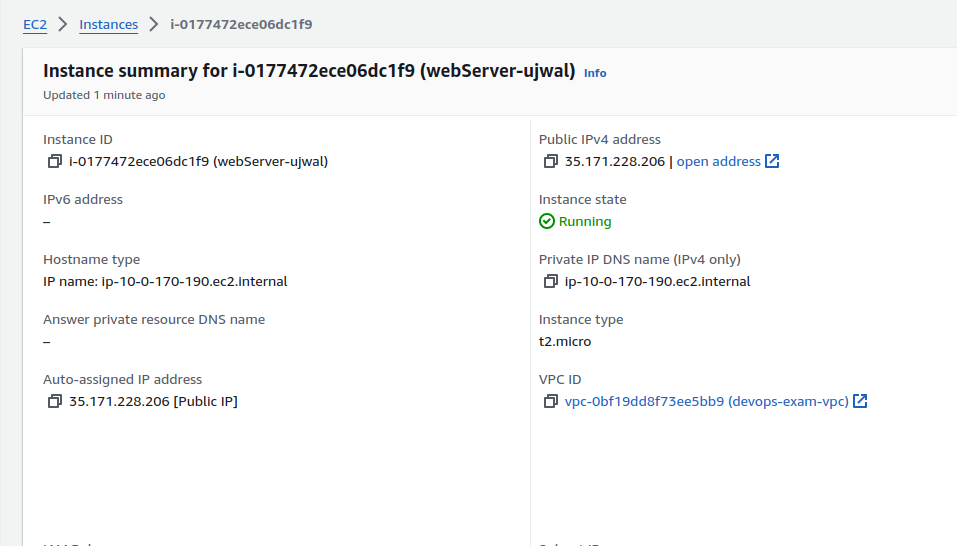
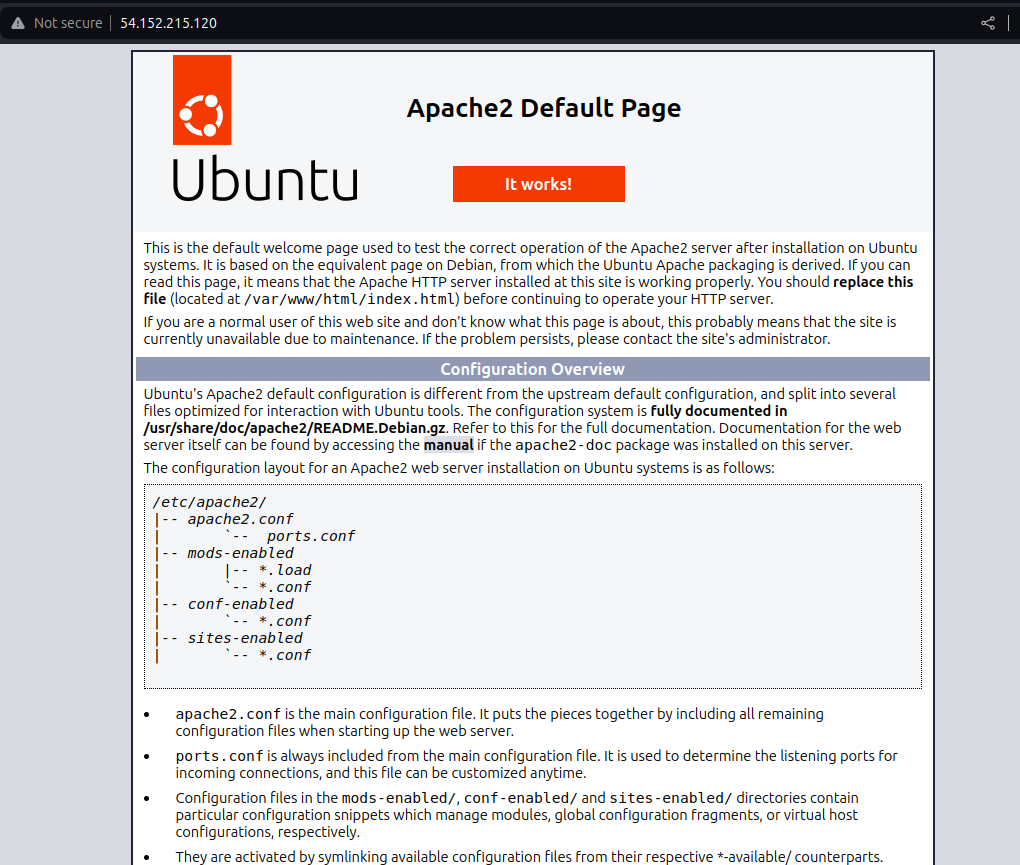
Open a browser and navigate to your instance's public IP address. You should see the default Apache page, confirming that the server is running:
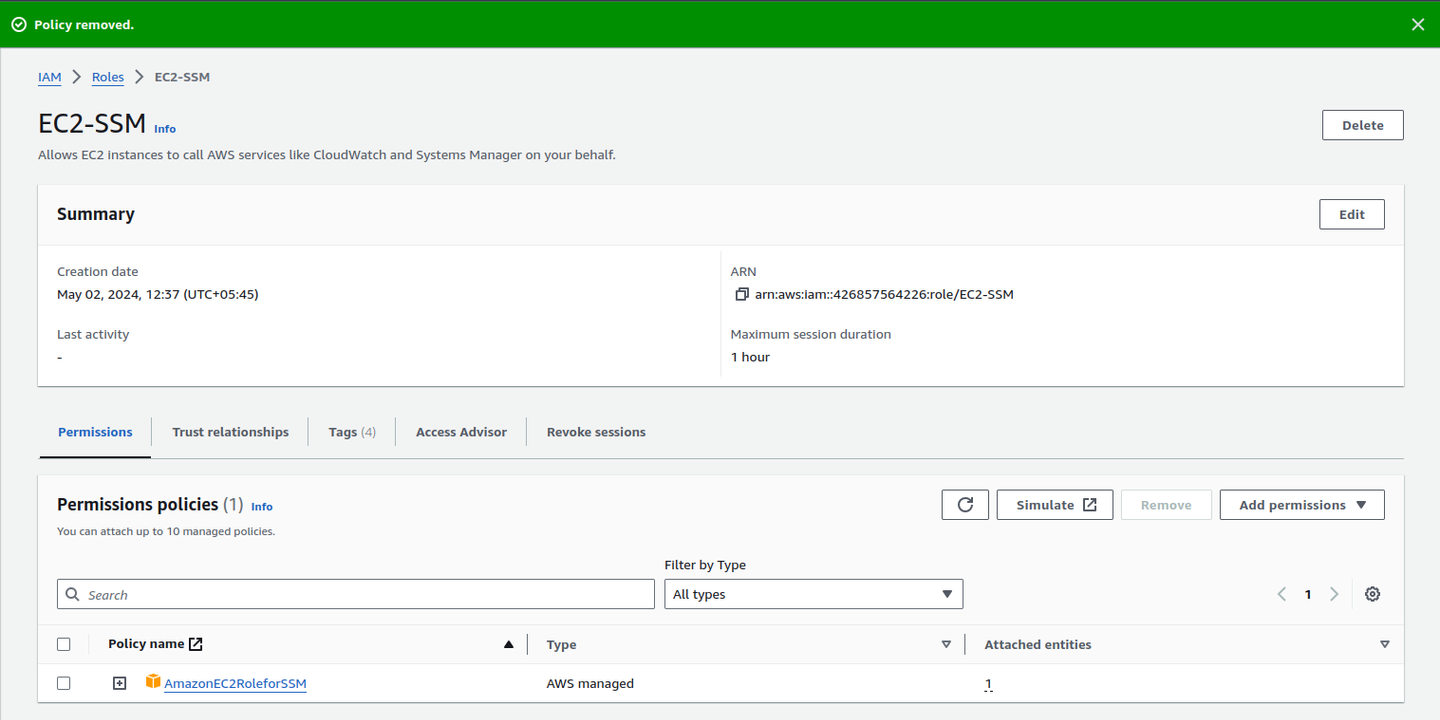
Systems Manager (SSM) allows you to manage your EC2 instances without requiring SSH. Attach the
AmazonEC2RoleforSSM to your instance, enabling secure remote access:
Use the following command to start an SSM session:
aws ssm start-session --target --region us-east-1 Congratulations! You have successfully created and configured an EC2 instance, installed Apache, and secured it using SSH and SSM. With these skills, you can deploy scalable and secure applications on AWS. Keep exploring to master more advanced AWS features.